How AI Agents Think, Act, and Learn: A Complete Guide
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has evolved significantly from a futuristic concept to a powerful tool that shapes our daily lives. Behind the scenes of most intelligent systems lies a core concept: the agent. Agents in artificial intelligence act as the decision-makers that observe, analyse, and act upon their environment to achieve a goal. From virtual assistants to autonomous vehicles, AI agents form the backbone of automation and intelligent problem-solving.
What Are Agents in Artificial Intelligence?
An agent in artificial intelligence is an entity that perceives its environment through sensors and acts upon that environment using actuators to achieve a specific goal. In simpler terms, it’s the “thinker” and “doer” within an AI system. Every agent has two primary functions:
- Perception– gathering data from the surroundings.
- Action– making decisions and taking steps toward a defined objective.
For instance, in a self-driving car, cameras and sensors perceive traffic signals and pedestrians, while the onboard system makes driving decisions such as accelerating or braking.
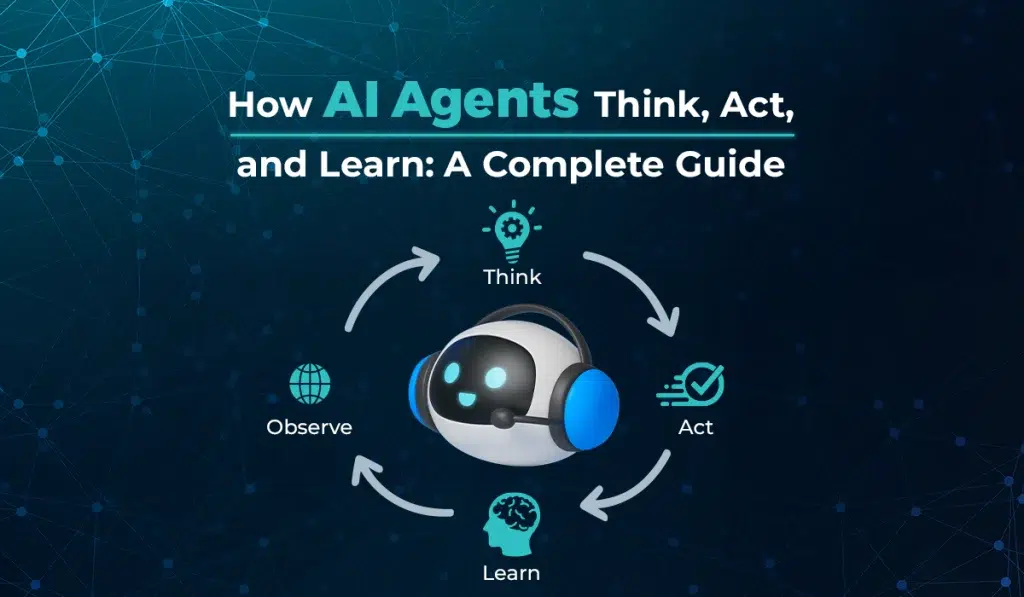
How AI Agents Work
The working principle of AI agents is based on a perception-action cycle. The agent continuously interacts with its environment, learning from inputs, applying logic or learned patterns, and optimising its actions over time.
In many modern systems, AI agents also utilise feedback loops, meaning they adjust their future actions based on the outcomes of their previous actions. This adaptability makes them valuable in industries such as customer service, logistics, and digital communication, where Tricall’s AI-driven solutions help businesses automate responses and enhance customer engagement intelligently.
Types of Agents in Artificial Intelligence
AI agents can be classified based on their complexity, capabilities, and the level of intelligence required to perform their tasks. Let’s explore the five primary types:
1. Simple Reflex Agents
These are the most basic types of AI agents. They function purely on condition-action rules, meaning they respond to specific inputs with predefined outputs.
Example: A thermostat that turns on cooling when the temperature rises above a certain level.
Although limited in their learning ability, these agents are reliable for repetitive and predictable tasks.
2. Model-Based Reflex Agents
Unlike simple reflex agents, model-based agents have a partial understanding of their environment. They use internal models to interpret the current situation and predict outcomes.
Example: A chatbot that maintains conversational context.
Tricall’s AI-powered communication tools leverage this model-based approach to provide context-aware responses, thereby enhancing the customer experience in every interaction.
3. Goal-Based Agents
Specific goals rather than fixed rules drive these agents. They evaluate multiple possible actions and choose the one that best achieves their target outcome.
Example: Navigation systems, such as Google Maps, calculate routes based on factors including traffic, distance, and time.
Goal-based agents are crucial where decision-making involves trade-offs or multiple options.
4. Utility-Based Agents
Utility-based agents take goal-based behaviour further by considering not just what to achieve but how well to achieve it. They use a utility function to measure the level of satisfaction or success associated with an outcome.
Example: Autonomous drones selecting the most energy-efficient route while avoiding obstacles.
These agents are commonly found in optimisation and resource management systems.
5. Learning Agents
Learning agents are the most advanced type of agent. They continually improve their performance over time, leveraging data and experience. Through techniques such as reinforcement learning, they adapt to new situations without requiring explicit programming.
Example: Voice assistants like Siri and Alexa that learn user preferences.
Tricall integrates this type of intelligent learning into its customer interaction platforms,
enabling businesses to automate communication that becomes smarter and more accurate over time.
Real-World Examples of AI Agents
Here are a few practical examples of AI agents in action:
- Customer Service Chatbots– Respond instantly to customer inquiries, providing 24/7 support with conversational accuracy.
- Recommendation Engines– Platforms like Netflix or Spotify use intelligent agents to suggest content based on user behaviour.
- Autonomous Robots– Used in manufacturing and delivery, these agents perform complex tasks without human intervention.
- Smart Assistants– Devices like Google Home act as personal assistants by understanding commands and completing actions.
- Business Communication Tools– Tricall’s AI-driven communication ecosystem enables automated call routing, data analysis, and customer engagement powered by intelligent agent technology.
Applications Across Industries
The use of agents in Artificial Intelligence extends across various sectors:
Healthcare
AI agents assist doctors by analysing patient records, predicting diseases, and suggesting treatment options.
Finance
Banking systems utilise AI agents to detect fraud, automate trading, and efficiently manage customer queries.
Retail and eCommerce
From personalised product recommendations to customer support automation, AI agents elevate user experience.
Transport
Autonomous vehicles rely on complex agents that continuously perceive, plan, and act safely in dynamic environments.
Business Communication
Platforms like Tricall demonstrate how AI agents streamline communication workflows, manage call routing, and provide insights that help businesses respond faster and more efficiently.
Benefits of Using AI Agents
- Automation of Repetitive Tasks– Reduces manual workload and enhances productivity.
- Real-Time Decision Making– Agents can process and respond faster than humans.
- Personalisation– Learning agents tailor experiences to user preferences.
- Error Reduction– Systems make data-driven decisions, minimising human errors.
- Scalability– Businesses can handle higher workloads without additional staff.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While AI agents offer immense benefits, they also present challenges, including data privacy concerns, algorithmic bias, and dependency risks. Organisations like Tricall focus on designing transparent and ethical AI frameworks to ensure automation doesn’t compromise fairness or user trust.
Developers and businesses must also consider how much autonomy to grant these agents and maintain human oversight in critical decision-making processes.
Empowering Smarter Systems with Tricall
The evolution of AI agents is transforming how systems learn, communicate, and solve problems. At Tricall, intelligent agents are integrated into communication platforms that understand, learn, and respond, enabling businesses to create more efficient customer experiences while maintaining the human touch.
Whether it’s optimising workflows, analysing real-time data, or delivering seamless automation, Tricall’s AI innovation empowers organisations to harness the full potential of
Artificial Intelligence responsibly and effectively.
FAQs About Agents in Artificial Intelligence
1. What are agents in Artificial Intelligence?
Agents are entities in AI that perceive their environment and take actions to achieve a goal, often using sensors and actuators.
2. What are the main types of AI agents?
The five main types include simple reflex agents, model-based agents, goal-based agents, utility-based agents, and learning agents.
3. How do learning agents improve over time?
They utilise data and experience through methods such as reinforcement learning to adapt and make better decisions with each iteration.
4. Where are AI agents used in real life?
They’re found in chatbots, self-driving cars, recommendation systems, healthcare analytics, and business automation tools like Tricall.
5. Why are AI agents important for businesses?
They enhance efficiency, enable data-driven decisions, automate communication, and create personalised customer experiences at scale.
